Gcp: разбор вычислительного стека google cloud platform
Содержание:
- Cloud advantages for business departments
- Что понимают под cloud computing?
- Cloud services vs. on-premises servers
- Примечания
- Как пользоваться облаком Яндекса
- Основные виды сервисов, предоставляемых на базе cloud computing (cloud services)
- Cloud technologies in business
- Some use-cases of cloud
- Как пользоваться облаком в интернете
- 2013: Cisco обходит HP и IBM на рынке оборудования для облачных решений
- Some more details about clouds
- What is cloud technology?
- 2014
Cloud advantages for business departments
Proper use of cloud-technologies will ensure the efficiency of all departments within the entire enterprise. Considering the benefits of cloud-based deployment of corporate systems and apps in the cloud, we focused on common points. Here below, a few examples of how different corporate departments can gain from the clouds:
Sales and Marketing Departments:
- sales managers get all the necessary information from any device any time from everywhere;
- optimization of decisions and sales;
- customer behavior prediction;
- marketing strategy planning;
HR Department:
- streamline workflow and collaboration through shared access to information;
- the more convenient process of recruitment, motivation, dismissal, retention of employees;
- professional training of employees, talent development, testing and level-up of skills and competencies in a convenient format on the job;
Customer Service:
- self-service is available to customers; it reduces the load on operators;
- centralization of the database;
- combining all operations of interactions with the customer.
It is just the tip of the iceberg — each company, each department has its points to add to the list of advantages of a cloud-based corporate IT system.
Что понимают под cloud computing?
Термин cloud computing переводят как «вычисления в облаках» или «облачные вычисления».
Концепция облачных вычислений заключается в предоставлении конечным пользователям удаленного доступа к динамично масштабируемым вычислительным ресурсам, услугам и приложениям (включая операционные системы и инфраструктуру), поддержку и обновление которых осуществляет провайдер услуг.
Фактически, технология cloud computing позволяет компаниям получить доступ к бизнес-приложениям при помощи интернета, что особенно актуально для небольших организаций, ограниченных в IT-ресурсах, стартапов и крупных корпоративных заказчиков, заинтересованных в гибких, легко масштабируемых решениях.
Cloud services vs. on-premises servers
The advantages of the new technology are not immediately well visible to everyone. But over the past decade, most IT experts agreed that moving business into a cloud is a reasonable decision. Successful cases of industry colleagues and competitors, who migrated their IT infrastructure to the cloud, convince companies to reconsider their attitude to cloud technologies.
At first glance, it’s more convenient to have an on-premises server or even a data center. But after more deep analyzing, we’ll see that the issues of equipment purchasing and depreciation, backup and storage for data archives, fault-tolerance and high-availability of services, ensuring information and physical security of servers and corporate data, maintenance of IT staff, systems and software updating, and many others aspects make up a massive layer of problems. To solve all of them you will spend a lot of time and investment. Sure, it would be much better to redirect this resource to the core business activities!
In contrast to on-premises hosting, the enterprise cloud infrastructure has a lot of undeniable advantages:
- 24/7 accessibility — access to information stored in the cloud round-a-clock from everywhere can get every user of a corporate IT system connected to the Internet;
- Access regardless of the hardware platform — user can connect to a cloud from any device, either a personal workstation or a laptop as a thin client, or a tablet, or a smartphone;
- Mobility — users can connect to the corporate system in the cloud from everywhere in the world where the Internet is available. It is a very convenient capability for company employees to hold online meetings, work remotely, receive and update information while on a business trip, and even solve urgent problems while on sick leave or vacation;
- Cost-effectiveness — the corporate IT expenditure transform from CapEx to OpEx. Since there is no need to keep expensive hardware and software on the company’s balance sheet, maintain a staff of engineers and technicians to support on-premises equipment, spend money on electricity and cooling servers. When the company’s infrastructure is deployed in the cloud, the customer pays only for the rental of computing resource capacities and the software licenses rent, if necessary;
- Flexibility — while a cloud project is creating together with the consultants of the provider, the company can determine the actual need for resources. If necessary, these resources can be increased, but if they are not in demand, they can be reduced, which will avoid overpayments for idle capacities. Such scaling in the conditions of cloud hosting is much faster and more economical than in the case of on-premises servers;
- The professional equipment — to solve the business tasks with the highest performance, you should use the server and network equipment of an enterprise-class. It is not difficult for a cloud provider to purchase such equipment and host it in a datacenter. Moreover, the provider ensures all the necessary conditions for the long-term working of many industrial-format servers in the professional datacenter. For most companies, this kind of IT expenditure is too expensive and inefficient. So it’s much cost-effectively to rent the required amount of resource capacity in the provider’s cloud;
- Reliability — state-of-the-art, top-notch cloud providers can ensure the outstanding high-availability, security, stability of the equipment. It is due to the ability to purchase and maintain professional equipment, and the conditions in the datacenter, necessary for fault-tolerance, redundancy, and continuous operation of the servers. Besides, a cloud provider uses advanced information security tools for data transfer and storage in the cloud. Moreover, if the cloud is deployed in Germany datacenters, the reliability of your infrastructure solution increases significantly due to the strictest law protection. And customizing of data backup transfer to remote storage will protect your critical business data perfectly.
Примечания
- Cloud IT Infrastructure Spending Grew 12.4% in the Fourth Quarter, Bringing Total 2019 Growth into Positive Territory, According to IDC
- Cloud IT Infrastructure Revenues Surpassed Traditional IT Infrastructure Revenues for the First Time in the Third Quarter of 2018, According to IDC
- Share of Spending on IT Infrastructure Continues to Shift to Cloud IT Environments at an Accelerated Rate in 2017, According to IDC
- Battle Intensifies for Cloud Infrastructure Leadership as Q4 sees Three-Way Tie
- Worldwide Cloud IT Infrastructure Spend Grew 21.9% to $29.0 Billion in 2015, According to IDC
- Cisco Maintains Lead in Public Cloud Infrastructure while HP Leads in Private
Как пользоваться облаком Яндекса

Яндекс.Диск – это универсальный интерфейс и портал для доступа к большинству популярных сервисов Яндекса. Недавно облако было оснащено офисным пактом приложений для работы с текстовыми документами, электронными таблицами, презентациями. Здесь же можно пользоваться календарем, почтой и электронным кошельком Яндекс.Деньги.
Если у вас уже есть почтовый ящик и адрес электронной почты Яндекс – вам не потребуется дополнительная регистрация, можете прямо заходить в облако со своим паролем и логином.
Бесплатно предоставляется 42GB памяти для хранения файлов.
Важно напомнить, что при пользовании бесплатной облачной памятью плату за интернет-трафик никто не отменял. Хранение телесериалов и просмотр видео непосредственно с облачного диска может довести ваши персональные финансы до дефолта
Ну, разве что смотреть мыльные оперы в рабочее время на служебном компьютере.
Для удобства можно скачать и установить приложения Яндекс.Диска для стационарного компьютера, мобильных устройств на платформах iOS или Android, Windows Phone.
С помощью облака можно наладить обмен файлами и совместную работу над документами, проектами в удаленном режиме. Для этого в параметрах файла нужно установить уровни доступа для других пользователей – только чтение, скачивание, редактирование.
Часто облачные хранилища используются для распространения каких-либо документов во всемирной сети. Для этого нужно в интерфейсе облака взять ссылку на файл и опубликовать в соцсети, на форуме, в блоге.
Основные виды сервисов, предоставляемых на базе cloud computing (cloud services)
IaaS (инфраструктура как сервис)
— это предоставление компьютерной инфраструктуры как услуги на основе концепции облачных вычислений. Вместо закупки и самостоятельного обеспечения работы физических серверов заказчик получает возможность управлять виртуальными серверами, работающими на оборудовании поставщика услуг. Мы предлагаем две услуги категории IaaS:
- Облачный сервер
- Облачный ЦОД
PaaS (платформа как сервис)
— предполагает наличие готовой к работе виртуальной платформы – средства для разработки приложений в облачной середе. Для работы с удаленной платформой компании не требуется устанавливать никакое дополнительное программное обеспечение. Все необходимое доступно через обычный браузер. Наиболее известными платформами для разработчиков являются Google Apps Engine, Apple iPhone Apps, Microsoft Windows Azure.
SaaS (приложения в виде сервисов)
— предоставление программного обеспечения как услуги, воспользоваться которой можно удаленно через интернет. В качестве наиболее очевидных примеров SaaS можно привести почтовый сервис Gmail и Google Calendar.
Преимущества сloud services для бизнеса:
- нулевые капитальные затраты;
- оперативная масштабируемость;
- снижение издержек на поддержку сервисов;
- автоматическое обновление программного обеспечения;
- доступность из любого места, где есть интернет;
- невысокая ежемесячная плата;
- высокая надежность;
- разнообразные формы оплаты.
Использование сloud-технологий позволяет снизить финансовые риски при старте нового проекта. Вы не затрачиваете средства на оборудование и программное обеспечение, что в случае неудачи позволяет сделать ваши потери минимальными (они ограничатся только абонентской платой за период использования сервисов).
Cloud technologies in business
Does the state-of-the-art business need clouds? Eight or ten years ago, owners and CEOs of enterprises of various sizes and business areas were seriously puzzled over this question. The concept “the safest solution is your on-premises bare-metal” was trendy at that time, and remote workplaces considered as something exotic.
Over the past several years, technology has raised far forward, and user awareness of cloud solutions became much more extensive. And now many users will confidently answer — sure, business needs clouds!
So we faced a range of more detailed questions:
- What Cloud is better — either private or public?
- What is a hybrid infrastructure, and why is it needed?
- How to choose a reliable cloud provider?
- How to ensure the security of your cloud project?
- What type of cloud solutions can meet all my requirements?
- Is a cloud project implementation costly?
Business owners and CFOs are very concerned about the security of the financial data of the company. You can learn how to provide it by moving the ERP system to the Cloud, reading in our article Why does ERP system feel better in the Cloud?
Not so far long ago, not only business owners but also many IT professionals were wary of the clouds. It was due, firstly, to a certain conservatism — after all, old and time-tested methods always seem more reliable than ambitious new ideas. Secondly, a lack of competent experts and professional information for some time formed mythologized ideas about cloud infrastructures in society. Thirdly, the early stages of technology sometimes generated to disappointments and negative experiences.
However, the time has put everything in its place. Enterprises at last fully appreciated the flexibility, cost-effectiveness, usability, and many other advantages of cloud solutions. In a digitalized world, the expectations and needs of customers, partners, and company employees are growing exponentially, and traditional IT systems are no longer able to meet them. The choice was made in favor of future technology, cloud solutions.
Some use-cases of cloud
We started this article from the question, «Does a business need clouds?» But the more actual question should be formulated this way: «Why business needs clouds?» What customers’ needs can meet the cloud-based IT infrastructure? Some enterprises are aimed to save costs; for some, the security is crucial, some companies are focused on processes optimizing. Each business decides this task depending on its business segment, on the size of the company, its strategy, the organizational structure, and even regulatory requirements.
For example, a financial institution cannot move all its systems to the cloud, since a massive pool of customers’ personal data requires specific security guarantees to preserve bank secrecy. However, its non-critical applications that don’t have a connection with the customer base — e.g., a website or a corporate university — are quite able to be deployed in the cloud.
In other words, it’s entirely optional to migrate to the cloud all the systems and apps of the company — only a few ones can be selected. Let’s look at some simple use cases for cloud-based business solutions.
Use case 1: Backup storage
This is the simplest option — to take backup data storage to the cloud. Backup experts advise storing copies of critical data remotely. A perfect solution — if your cloud storage deployed in a European datacenter, where data is transferred via secure encrypted channels, and data on storage drives is protected by hardware-based encryption. If necessary, you can ask your provider and recover data from backups remotely in the cloud. Thus, you will create a «clone» of your corporate infrastructure.
Use case 2: Stand-by Area
It is too expensive to arrange on-premises a redundant infrastructure with high-availability. So, instead of building your server cluster (in fact, it will be on-premises data center), use the cloud to organize a stand-by area. Companies use this option both in the SME sector and large corporations.
Use case 3: Resource capacity for peak loads
If your business has seasonally or time-to-time distributed loads, you can deploy in the cloud the apps that are used in a highly loaded period. Yes, this way, you create a hybrid cloud for your company! Numerous tools for integrating local and cloud applications on the market will ensure the effective operation of such an infrastructure.
Use case 4: Test and deployment environment for demanded projects
In companies with an extensive organizational structure, individual teams are involved in the development of projects demanded by business. Before starting a project, a resource audit should take into account everything, to the smallest detail, including space for product deployment. In spherical IT in a vacuum, this is done, but in our reality, it is rare. So, if the business dept is waiting for the application, but there are not enough on-premises computing resources for it, the cloud can help. Perhaps this decision even will help your final product exceed expectations.
You can read more about business cloud use scenarios in our article 3 apparent advantages to deploy infrastructure in a public cloud.
Use case 5: Cloud migration of all corporate infrastructure
The cloud migration of the entire IT infrastructure to abandon a bare-metal on-premises is a classic option that is usually considered. It allows you to fully experience all the advantages of cloud technologies, which we described above. The provider takes care of the cloud migration of customer systems and tries to organize the relocation work in such a way as to minimize the impact on the business. The team of infrastructure engineers SIM-Networks, for example, pre-analyzes the workload of a customer and transfers its infrastructure to the cloud when downtime will be minimal. By the way, we do it for free. You can learn about how we implemented some of projects implemented by the SIM-Networks team from Business Cases and Our Customers’ Stories.
Как пользоваться облаком в интернете
Использование облачных сервисов происходит по принципу Кота Матроскина: «Корова колхозная, мы ее взяли в аренду, поэтому все, что она дает – наше». Так и с облаком, клиент входит в сервис через программу-клиент, производит некие вычисления и может забрать себе полученные результаты.
Облачные сервисы бывают бесплатные, условно-бесплатные и коммерческие. Полностью платные облачные сервисы обычно предназначены для нужд бизнеса – инфраструктурные решения, системы удаленного менеджмента производственными и торговыми процессами, CRM, сервисы статистики и аналитики, коммерческая электронная почта, бухгалтерские базы 1С.
В последнее время к облачному формату перешли такие популярные разработчики ПО, как Adobe PhotoShop. Серия профессиональных приложений для работы с графикой, ранее работавших в виде устанавливаемых приложений, теперь распространяется по подписке, с периодический абонентской платой за доступ к облаку.
Бесплатные SaaS предназначены для сугубо домашних, мирных целей, но иногда лицензией не возбраняется извлечение коммерческой выгоды.
- Бесплатные хранилища пользовательских файлов.
- Менеджеры паролей (LastPass).
- Офисные пакеты приложений (Google Docs).
- Приложения для создания инфографики, фоторедакторы, видеостудии, сервисы для создания инфографики, веб-баннеров, GIF-анимации, платформы для разработки и публикации веб-сайтов и блогов.
- Онлайн-сервисы для сбора статистики, анализа, структурирования и представления данных в форме отчетов, графиков, таблиц и диаграмм.
Облачные решения удобны и выгоды в том смысле, что нет необходимости приобретать дорогостоящее лицензионное программное обеспечение для выполнения разовых задач. Можно заказать ровно тот объем сервисов, какой необходим для дела, когда это необходимо.
2013: Cisco обходит HP и IBM на рынке оборудования для облачных решений
В начале 2013 года Cisco удалось обойти HP и IBM по доле выручки от реализации оборудования для облачных решений в общей структуре доходов, и это при том, что сильнейшими игроками на «облачном» рынке являются другие вендоры. Однако, как следует из отчета Synergy Research Group, опубликованного в июне 2013 года, в первом квартале 2013 года Cisco Systems заработала на cloud computing 15% из вырученных за эти три месяца $9 млрд.
Для сравнения, доля оборудования для облачных решений в объеме выручки в первом квартале 2013 года у IBM и HP составила 14% соответственно, у Dell – 9%, у EMC – 7%, у VMWare – 4%, у NetApp и Oracle – 4% и 3% соответственно, заявил аналитик Synergy Research Group Джон Динсдейл (John Dinsdale).
Рынок оборудования для cloud computing, первый квартал 2013 года
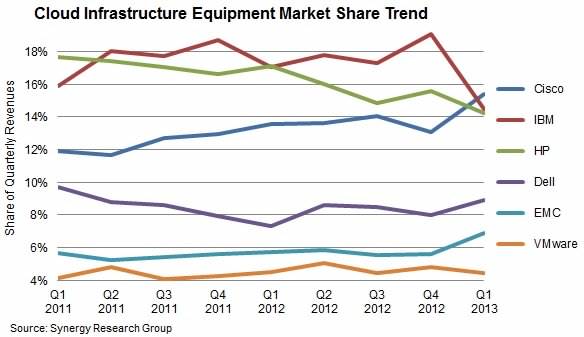
Synergy Research Group, 2013
Тем не менее, предупреждают эксперты, Cisco будет довольно сложно сохранить лидерство в этом сегменте, поскольку своим взлетом в начале 2013 года компания во многом обязана слабым результатам, которые показали серверные подразделения HP и IBM.
Впрочем, аналитики установили и еще один интересный факт: 30% расходов на «облачное» оборудование вообще минуют «карманы» мегавендоров и отправляются более мелким поставщикам. Все потому, что крупные интернет-компании, такие как , , Rackspace и другие предпочитают покупать не готовые серверы, а создавать свои собственные, договариваясь напрямую с производителями компонентов.
Согласно ранее опубликованным прогнозам IHS iSuppli, поставки облачных серверов достигнут 875 тыс. единиц в 2012 году, увеличившись на 35% по сравнению с 2011 годом и почти в два раза по сравнению с 2010 годом. Эксперты ожидают высокие темпы роста в пределах от 23% до 30% в течение каждого из последующих трех лет вплоть до 2015 года, когда общий объем поставок облачных серверов достигнет 1,8 млн единиц. Таким образом, облачные сервера будут составлять все большую часть от общего числа серверов, чьи поставки вырастут от чуть более 5% рынка в 2010 году до 15% в 2015 году, предполагают в IHS iSuppli.
Some more details about clouds
For last years, experts worry about the security issue of uncontrolled data in public cloud services — information left by the user, so-called digital footprint, can be stored for years without user’s permission and even behind his/her back. The leakage scandals concerned user data from Facebook, Google, and other large web resources have shaken the customers’ confidence in cloud security. And this triggered the emergence of one of the most common arguments against the cloud — «In the cloud, my privacy is not protected, my data can be stolen.»
Yes. All of us, as private users, are at risk. And we are forced to rely on the decency of those whom we trust our data. Besides, people often carelessly hold their private information.
But the information security of corporate IT systems and customers’ data, which delivers a cloud provider, is an entirely different layer of responsibility. Each provider has its ways to ensure cloud security. E.g., within the infrastructure projects implemented by SIM-Networks, data protection realized at three levels — technological (cryptographic algorithms, the hardware-based encryption of drives, etc.), legislative (protected by the Federal Republic of Germany Law), and physical (high-end datacenters certified in compliance with the Tier III and Tier III+ and ISO/IEC 27001). Besides, mandatory papers, as contracts, GTC, and SLA, protect the rights of the customer and guarantees the high-level service provided.
So, it is essential to choose the cloud infrastructure provider carefully. It is reasonable to consider the legislation of the country where the data is stored, the business goodwill, and the information security policy of the provider. Standard requirements include (but not limited to) the following scope of rules: all data should be stored only in encrypted form; data transfer between customer and cloud provides over secure communication lines; encryption keys should only be available to customers who own this information.
Anyway, a lot of enterprises agree that cloud technology is the trend-setter of the digitalized future. Because of its user experience, they have seen how the advantages of clouds increase its business efficiency.
Author: Alisa Kandieieva
What is cloud technology?
In simple words, cloud computing — is a model for providing users with network access to a pool of computing resources through an API or browser, regardless of geographic location and time of day.
The cloud service provider is responsible for: configuring a cluster cloud pool; combining server and communication equipment, software and applications, additional services, storage systems, networks, etc. to an entire infrastructure; as well as ensuring system high-availability, fault-tolerance; stable connection to ISPs; information security of resources and users’ data; support, maintenance, and upgrades of equipment and software, so on.
Users get access to cloud resources by renting a configuration of computing power that can be flexibly scaled (expanded or reduced) on-demand, depending on the current needs of the customer.
Nowadays, the cloud services market offers customers a wide range of infrastructure solutions:

- Public cloud (IaaS) — a multitenant pool of computing resource capacities located at the provider’s datacenter. Each customer gets part of computing resources and storage, depending on his/her needs. All clients in the public cloud are isolated from each other;
- Private cloud — a single-tenant, turnkey infrastructure, built for an individual client. The individual project of a private cloud takes into account business conditions, high-availability and fault-tolerance ensuring, data backup, scalability, information security, and other necessary options;
- Hybrid cloud — the infrastructure solution that distributes of company’s computing capacities and data between a public cloud and a private, either on-premises servers. Within the hybrid cloud, systems and applications with a stable load are deployed in the provider’s private cloud or deployed on a local server cluster, and services with distributed over time dynamic loads are transferred to the public cloud;
- Multicloud is a technological concept that is still gaining popularity in the IT world — the enterprise hosts its infrastructure in several public clouds of various providers. It is a complicated solution, both technologically and conceptually, and economically and from a security point of view. It requires an extraordinary strategic vision from the business and strict criteria for choosing providers. Nevertheless, companies have been actively implementing a multicloud for several years.
The choice of infrastructure solution depends entirely on the business specifics, its needs, its size. Note that the cloud infrastructure should match your company as a perfectly tailored suit for a gentleman. So, each cloud solution for each client needs to be provided individually.
Cloud solutions did not appear in the blink of an eye. Like any natural phenomenon, like any human invention, cloud technologies went through several stages of development, which were preceded by the creation of the Internet and the discovery of virtualization technology. These stages have now turned into cloud service models, and you can learn more about them in our article Cloud Service Models: What does IaaS, PaaS, SaaS mean?
2014
Доходы EMC от решений для ЦОДов взлетели на треть. HP отступает
16 апреля 2015 года аналитическая компания IDC опубликовала результаты исследования глобального рынка облачных инфраструктур. Его объем в 2014 году вырос на 18,7%, а лидерство HP ослабло.
Как сообщается в регулярной сводке IDC Worldwide Quarterly Cloud IT Infrastructure Tracker, в 2014 году продажи серверов, систем хранения данных и Ethernet-коммутаторов, приобретенных для развертывания облачных инфраструктур, составили $26,4 млрд против $22,3 млрд годом ранее.
Расходы на оборудование для публичных облаков увеличились на 17,5%, достигнув $16,5 млрд. В сегменте частных облачных сервисов реализация оборудования поднялась на 20,7% до $10 млрд.
По данным экспертов, в четвертом квартале 2014 года мировые затраты на оборудования для запуска публичных и частных облачных сервисов составили 30% от суммарных инвестиций компаний в ИТ-инфраструктуры. Годом ранее этот долевой показатель измерялся 27%.
Как считает Ричард Вилларс, ключевым драйвером подъема рынка облачных инфраструктур являются сервисы «интернета вещей», требующие того уровня гибкости и масштабируемости, который обеспечивают лишь облачные решения.
В 2014 году тройка крупнейших производителей решений для облачных инфраструктур не претерпела изменений, но позиции лидера HP ослабли. Выручка компании на рассматриваемом рынке выросла на 6,3% до $3,7 млрд, что соответствует 15,7% в глобальных продажах облачного оборудования против 17,4% годом ранее.
|
Vendor |
Выручка 2014 млрд долл. |
Доля 2014 |
Выручка 2013 млрд долл. |
Доля 2013 |
Рост выручки в 2014 |
|
1. HP |
$3,7 |
15,7% |
$3,5 |
17,4% |
6,3% |
|
2. Dell |
$2,6 |
10,7% |
$2,4 |
11,8% |
7,2% |
|
2. Cisco |
$2,1 |
8,7% |
$1,7 |
8,5% |
21,2% |
|
4. EMC |
$1,9 |
8,0% |
$1,4 |
7,1% |
34,3% |
|
5. IBM |
$1,7 |
7,3% |
$2,2 |
10,7% |
-18,9%* |
|
ODM |
$6,6 |
27,8% |
$4,8 |
23,9% |
37,3% |
|
Другие |
$5,2 |
21,7% |
$4,2 |
20,7% |
4,7% |
|
Общие |
$23,9 |
100% |
$20,2 |
100% |
17,9% |
Крупнейшие производители оборудования для облачных инфраструктур, данные IDC за 2014 г.
Снижение рыночной доли HP связано с активностью конкурентов. К примеру, Cisco и EMC в 2014 году увеличили реализацию оборудования для облачных инфраструктур на 21,2% и 34,3%. Это позволило компаниям приблизиться к Dell, занимающей второе место в списке вендоров.
Microsoft вошла в тройку крупнейших поставщиков облачных инфраструктур
12 марта 2015 года аналитическая компания Synergy Research Group опубликовала исследовательский отчет по мировому рынку решений для развертывания и обслуживания облачных инфраструктур. К этим продуктам эксперты относят серверы, сетевые и вычислительные платформы, а также ресурсы хранения данных.
По оценкам аналитиков, в четвертом квартале 2014 года продажи оборудования и программного обеспечения для облачных инфраструктур в глобальном масштабе составили более $13 млрд, что на 9% больше, чем по итогам последних трех месяцев 2013 года.
Лидерство на рассматриваемом рынке сохраняют Cisco и HP, совокупная доля которых измеряется 27%. Однако в годовом исчислении данный показатель снизился, поскольку рост продаж у этих компаний оказался ниже, чем в среднем по рынку.
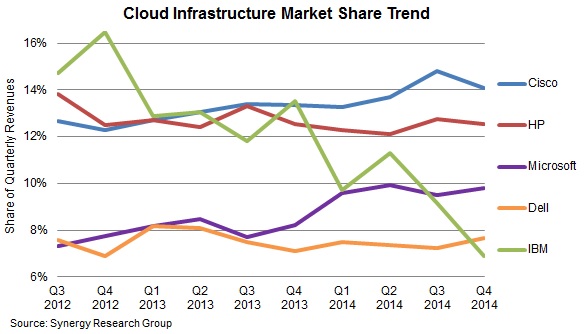
Microsoft вошла в тройку крупнейших поставщиков облачных инфраструктур
Cisco является крупнейшим производителем в сегменте публичных облачных инфраструктур, тогда как HP занимает первое место по поставкам решений для частных облаков.
Общее доминирование Cisco во многом связано с тем, что компании практически нет равных с точки зрения размера продаж сетевого оборудования. Кроме того, вендор стремительно укрепляет позиции на глобальном рынке серверов, где доля Cisco выросла до 5,3% в 2014 году (данные IDC).
Как сообщают в Synergy Research, корпорация HP лидирует по поставкам облачных серверов, а также является крупным поставщиком дисковых хранилищ и растущим конкурентом Cisco на рынке сетевого оборудования.
Microsoft удерживает пальму первенства среди разработчиков серверных операционных систем и входит в группу лидеров на рынке технологий виртуализации. В октябре-декабре 2014 года американская корпорация вошла в тройку крупнейших поставщиков решений для развертывания и обслуживания облачной инфраструктуры, по данным аналитиков Synergy Research, оставив позади Dell и IBM.
Последняя, стоит отметить, была лидером рынка в конце 2012 года, однако за два года растеряла свои позиции. Весомую роль в этом сыграла продажа части серверного бизнеса компании Lenovo, которая благодаря сделке взобралась на седьмое место в списке производителей оборудования для облаков.